I know it’s been like a really long time — sorry about that! My real life job got absolutely crazy and hasn’t calmed down at all. May not ever calm down but I’m handling the craziness better now that I’m kind of getting used to it. So….we’re back with even more queer history!
Chances are pretty good, if you’re an LGBTQIA+ person you’ve been to a gay bar. Even if you’re just someone who loves an LGBTQIA+ person, there’s still a good chance you’ve been to a gay bar. I’m not saying you’re doing queerness wrong if you haven’t been to a gay bar, I’m just saying it’s a pretty common shared experience. It’s true that bars being basically the central gathering place for our community isn’t without drawbacks — although, personally, I love them. But I’m not here to weigh the pros and cons of gay bars — we can all do that on Twitter (and we do) — I just want to talk briefly about the history of gay bars, talk a teeny bit about some of the first ones to exist, and some of the oldest ones that we still have today. A lot of these places will hopefully get posts of their own further down the line.
We have previously talked a little about molly houses before — specifically Mother Clap’s and the White Swan, which were both pretty historically significant. Gay bars were not, at least initially, all that different from molly houses and, in terms of their purpose, still aren’t. They’re a place for gathering socially with similar “deviants” and “sodomites,” to feel safe among those who have a shared lived experience. To separate molly houses from gay bars, we have to kind of look at the history of bars themselves. For a lot of (at least Western) history, bars weren’t really a thing — you had inns and taverns, which served alcohol but also offered lodging or food. Even pubs at the time served food and were intended as a place to have gatherings or meetings. The sale of alcohol was considered sort of a “side hustle” (even though it was probably where most of the profit came from.) Even saloons in the American western frontier were entertainment sites — where people could play games or see performances. Molly houses were typically fronted by taverns, inns or coffee houses, and usually also made money off prostitution. They were also places where fake weddings and mock birth rituals took place. So, to separate molly houses from gay bars — and I’m not going to claim this is the official definition, it’s just what I’m working with here — I’m going to define gay bars as legitimate, legal businesses focused entirely (or almost entirely) on the sale of alcohol to queer customers.
It wasn’t really until towards the end of the 19th century when there started to be bars as we know them today — places that really just served alcohol. I’d guess the invention of machines like the phonograph, which let places play music without having performers present, was probably a big part of that shift. So, of course, as mainstream society started socializing in these places, the queer community followed suit. And so gay bars began to pop up — the first, as far as we can tell was in Cannes, France (where homosexuality had been decriminalized since 1791.) That bar was Zanzibar, which was founded in 1885 and lasted 125 years — eventually closing in December of 2010.

Meanwhile, Berlin had also become a hotspot of gay and lesbian nightlife by 1900, thanks largely to the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee‘s presence there, though a lot of the specific records about these spots were lost thanks to the Nazis. Within weeks of the Nazi party taking power in Germany in 1933, fourteen gay and lesbian nightclubs were closed, including an internationally renowned drag bar called Eldorado.
The other issue for gay bars at the beginning of the 20th century was Prohibition. Several countries tried their hand at banning the sale of alcohol including Russia, Iceland, Finland, Canada, Norway and the United States. At least in the USA, the fact that everyone‘s bars became illegal and everyone’s drinking had to go underground — where we were already partying — had a pretty profound impact on the queer community. But the most lasting effect of Prohibition, at least for gay bars in the USA, was that alcohol sales became part of the world of organized crime. Even after Prohibition ended in the USA, most gay bars were run by the mafia for the next few decades. In fact, more than thirty years later, this was one of the issues that was raised and fought against during the Stonewall riots and their immediate aftermath.
Over the early decades of the 20th century, gay nightlife spread throughout Western culture. Here’s a few other highlights:
- The Black Cat Bar (not to be confused with the Black Cat Tavern) was founded in San Francisco, California in 1906, and stayed open until 1921. It reopened in 1933 when Prohibition ended, and continued operating until 1963. It might be the first gay bar in the United States.
- The first recorded mention of the then-popular Amsterdam gay club The Empire was in 1911, but it seems to have already been established several years prior. It closed in the 1930’s.
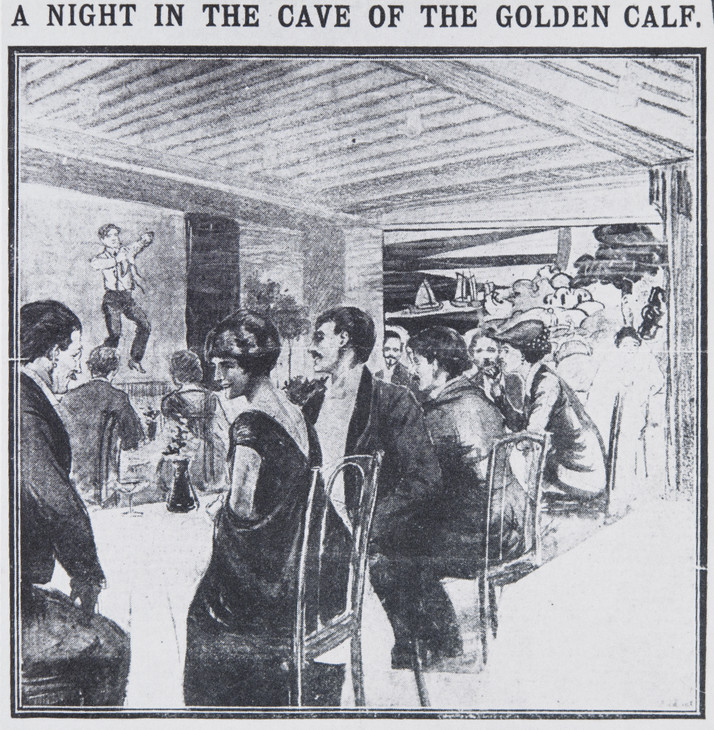
- The Cave of the Golden Calf, founded in 1912, was the first “official” gay bar in England, though it went bankrupt and closed in 1914. Still, it made a reputation for its wild parties and influenced a lot of gay bars afterwards.
- Eve’s Hangout in New York City was one of the first, if not the first, lesbian bar in the United States, opening in 1925 and closing at the end of 1926 due to police raids. This raid more or less led directly to owner Eva Kotchever‘s death at the Auschwitz concentration camp. (Which is definitely getting its own piece, don’t worry, I’m not just leaving you all with no details on that!)
- Social reforms brought about by President Lázaro Cárdenas of Mexico brought about the creation of roughly a dozen gay bars in Mexico after he came into office in 1934, including El Triunfo and El África in Mexico City. All of Mexico City’s gay bars were closed in 1959 and even though there are gay bars in the city now, none of the original ones reopened.
- The first gay bar in South Africa opened in the Carlton Hotel in Johannesburg in the late 1940’s — catering to wealthy white gay men. No women were permitted, and, you know keep in mind there’s Apartheid going on, so definitely no people of color, who were forced to create and use increasingly underground bars and clubs — unfortunately, there’s not too much available about those clubs at the time. However, some of these bars, such as the Butterfly Bar (now the Skyline) began to integrate in the mid-1980’s.
- The American occupation of Japan following World War II brought gay bars to the country — New Sazae opened in Tokyo during this period, in 1966, and is still open now.
- In the 1970’s, a lot of clubs in Singapore began having gay nights but no actual gay bars opened until the lesbian bar Crocodile Rock opened in the 1980’s. It is still open, and is the oldest gay bar in that country.
If you want to experience some history for yourself, here’s some of the oldest gay bars still around today:

- Atlantic House (or “A-House”) in Provincetown, Massachusetts was opened as a tavern in 1798, but mostly served whalers until the beginning of the 20th century, when it became a popular hangout for artists and writers like Eugene O’Neill and Tennessee Williams. They “officially” became a gay bar in 1950 (despite already being popular with gay men like, y’know, Tennessee Williams) and it still operates as one today. (And I’ll vouch that it’s still a fun place to go!)
- Café ‘t Mandje opened was opened in Amsterdam by a lesbian named Bet van Bereen in 1927, and continued to operate until the death of her sister Greet (who took it over after Bet passed away) in 1982. Her niece Diana reopened it on April 27, 2008 and it remains open today, still in the same family that started it!
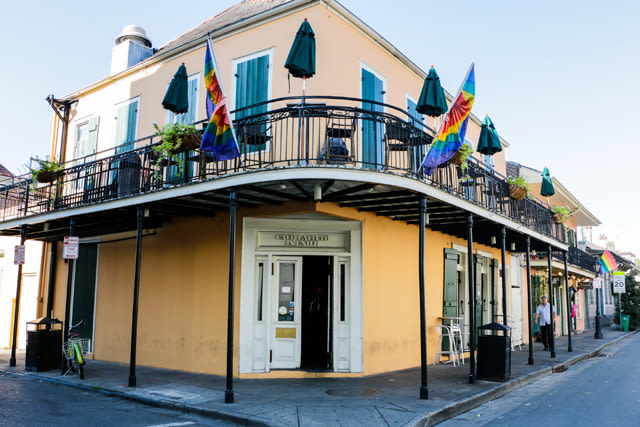

- In 1933, both White Horse Inn in Oakland, California and Café Lafitte in New Orleans, Louisiana opened (now called Café Lafitte in Exile after they were forced to move to a new spot in the city in 1953). I don’t know the exact months or days they were founded, so I can’t tell you which is actually older (and of course, they both claim to the be the oldest.) I’m trying to solve the mystery, and rest assured, I will even if it means I have to take a cross country road trip to both of them.
- The Double Header in Seattle, Washington opened up the next year and Korner Lounge in Shreveport, Louisiana opened sometime in the late 1930’s as well. Both are still open today.
- Mirabar opened in Woonsocket, RI in 1947. It’s moved around to number of different locations (it’s in Providence now, for starters), and is still open today. (And they have a great trivia game on Wednesday nights!)
- The Half-and-Half in Beijing is the oldest still-operating gay bar in China, having opened some time before 1994.
Some honorable mentions that aren’t really the “oldest gay bars” in their countries but are still historically important and that you can still visit today:
- Julius’ – Julius’ opened in Manhattan in 1864 but it was decidedly not a gay bar but by the late 1950’s, gay men started frequenting it but were often thrown out or simply refused service because it was illegal to serve homosexuals in New York City at the time. In 1966, Dick Leitsch and Craig Rodwell, president and vice president of the Mattachine Society at the time, organized a sip-in protest. By most accounts I’ve, the bartender refused them service to help them with the protest not because they were gay. Laws were changed and Julius’ has been serving gay customers ever since.
- Stonewall – the famous Stonewall Inn, which originally opened in 1967, has been through a lot since our riots — renovations, closing, reopening, closing again, hosting several other businesses, reopening again, closing again, reopening again…..they’ve dropped the word “inn” from their name, and have been open on Christopher Street in Manhattan since 2007.
- The Eagle – Eagles can be found in cities all over the world. They’re not franchises, they’re not a chain, they’re just connected by the community they serve. After the Stonewall riots, the owners of the the Eagle’s Nest (which had been open since 1931, and is now Eagle NYC) made their club a gay bar and it became a very popular spot for more masculine gay men, and especially the leather scene, to hang out. Other Eagles opened elsewhere, even in other countries, and “the Eagle” became a sort of code for gay men looking to connect to their community in a new city. Not every Eagle is historic, but they are all part of that legacy.
I know this breezes past a lot of fascinating details and there’s an awful lot of countries that didn’t get a mention — I simply haven’t found what their oldest gay bars were yet. But rest assured, I’m going to keep the “Raising the Bar” series going intermittently, so there will be lots more coming on this topic!





















 Oscar Wilde is arguably one of the most famous and lasting playwrights since William Shakespeare — and his work was popular to boot. He was a celebrity in his time, known even then for being an extremely quotable master of one-liners.
Oscar Wilde is arguably one of the most famous and lasting playwrights since William Shakespeare — and his work was popular to boot. He was a celebrity in his time, known even then for being an extremely quotable master of one-liners. At Magdalen College, Wilde reinvented himself. He explored several organizations, religions and philosophies. He toyed with joining Roman Catholicism — despite threats that his father would cut him off financially if he was baptized into that faith. Wilde ultimately decided, at the last minute, not to do it, and sent flowers to the ceremony in his place. He said he liked their aesthetic, rather than their beliefs. Wilde also replaced his Irish accent with an upper class British accent, began to dress in formal wear literally all of the time and lavishly decorated his room with peacock feathers. It was about this time — no surprise — that he became involved in the Decadent Movement.
At Magdalen College, Wilde reinvented himself. He explored several organizations, religions and philosophies. He toyed with joining Roman Catholicism — despite threats that his father would cut him off financially if he was baptized into that faith. Wilde ultimately decided, at the last minute, not to do it, and sent flowers to the ceremony in his place. He said he liked their aesthetic, rather than their beliefs. Wilde also replaced his Irish accent with an upper class British accent, began to dress in formal wear literally all of the time and lavishly decorated his room with peacock feathers. It was about this time — no surprise — that he became involved in the Decadent Movement. Wilde settled in London after graduating, though he spent a good amount of time in Paris. In 1881, a collection of his poems (now having been published in various places since roughly 1871) was published. The first print run of Poems was 750 copies — it sold out and had to have a second run printed in 1882. Despite the book’s undeniable popularity, reviews were mixed — the British magazine Punch was notably unenthusiastic. Their review stated: “The poet is Wilde, but his poetry’s tame.” (Don’t you sometimes wonder if people write intentionally bad reviews just so they throw in some solid gold zingers like that one?)
Wilde settled in London after graduating, though he spent a good amount of time in Paris. In 1881, a collection of his poems (now having been published in various places since roughly 1871) was published. The first print run of Poems was 750 copies — it sold out and had to have a second run printed in 1882. Despite the book’s undeniable popularity, reviews were mixed — the British magazine Punch was notably unenthusiastic. Their review stated: “The poet is Wilde, but his poetry’s tame.” (Don’t you sometimes wonder if people write intentionally bad reviews just so they throw in some solid gold zingers like that one?)
 Baron Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben was born in Magdeburg in the kingdom Prussia on September 17, 1730. His father was the Royal Prussian Engineer Captain Baron Wilhelm von Steuben and his wife Elizabeth von Jagdovin. In his childhood, his father went into the service of Empress Anna of Russia, and young von Steuben traveled with his father to his various posts. They returned to Prussia in 1740, where von Steuben began to a formal military education, taught to him by Jesuits. This education — despite being from a Roman Catholic order — left him extremely critical of the Roman Catholic church. This was probably partly because his parents were devout Protestants.
Baron Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben was born in Magdeburg in the kingdom Prussia on September 17, 1730. His father was the Royal Prussian Engineer Captain Baron Wilhelm von Steuben and his wife Elizabeth von Jagdovin. In his childhood, his father went into the service of Empress Anna of Russia, and young von Steuben traveled with his father to his various posts. They returned to Prussia in 1740, where von Steuben began to a formal military education, taught to him by Jesuits. This education — despite being from a Roman Catholic order — left him extremely critical of the Roman Catholic church. This was probably partly because his parents were devout Protestants. His training methods were also a hit — soldiers found him both impressive and entertaining, and found renewed confidence in themselves as they quickly mastered the tactics and maneuvers he instilled in them. He hand-selected 120 men (who became Washington’s honor guard) and trained them — mostly by barking at them, with Benjamin Walker translating. At a certain point, he began insisting that Walker translate not only his orders but also his (many) curse words. These 120 men, in turn, each trained other units of soldiers, who went on to train others, until the entire camp was trained. He had the entirety of the troops at Valley Forge trained by the end of April — just a few months after his arrival.
His training methods were also a hit — soldiers found him both impressive and entertaining, and found renewed confidence in themselves as they quickly mastered the tactics and maneuvers he instilled in them. He hand-selected 120 men (who became Washington’s honor guard) and trained them — mostly by barking at them, with Benjamin Walker translating. At a certain point, he began insisting that Walker translate not only his orders but also his (many) curse words. These 120 men, in turn, each trained other units of soldiers, who went on to train others, until the entire camp was trained. He had the entirety of the troops at Valley Forge trained by the end of April — just a few months after his arrival. Von Steuben Day is a holiday that occurs in mid-September every year and which celebrates German-American culture and contributions to the country — the New York Von Steuben Day Parade is one of the largest parades in New York City every year. Chicago also holds an impressive Von Steuben Day parade, which was featured in the movie Ferris Bueller’s Day Off. There is a also statue of him in Lafayette Square in Washington, D.C.
Von Steuben Day is a holiday that occurs in mid-September every year and which celebrates German-American culture and contributions to the country — the New York Von Steuben Day Parade is one of the largest parades in New York City every year. Chicago also holds an impressive Von Steuben Day parade, which was featured in the movie Ferris Bueller’s Day Off. There is a also statue of him in Lafayette Square in Washington, D.C.
 An important fact about the
An important fact about the  Working as a Navy cook, stationed in Brooklyn, Garvin began coming out of the closet. Coming out proved quite difficult, especially given his religious upbringing. Drunk and off the base one night, Garvin sought out the only other gay man his age that he knew of — but he was soundly rejected. Reeling, Garvin attempted suicide and then called a psychiatrist who told him to admit himself to Bellevue Hospital. The Navy transferred him to St. Albans Naval Medical Hospital.
Working as a Navy cook, stationed in Brooklyn, Garvin began coming out of the closet. Coming out proved quite difficult, especially given his religious upbringing. Drunk and off the base one night, Garvin sought out the only other gay man his age that he knew of — but he was soundly rejected. Reeling, Garvin attempted suicide and then called a psychiatrist who told him to admit himself to Bellevue Hospital. The Navy transferred him to St. Albans Naval Medical Hospital. Although on his first visit, Garvin was mostly shocked to see men dancing together, he became a regular and even dated the main doorman (“Blonde Frankie“) for a time. Though he was initially living on the streets and hustling for a living — an experience he would carry with him the rest of his life — he ultimately found his way into living in what David Carter describes in his book Stonewall: The Riots That Sparked the Gay Revolution as a “gay hippie commune.” Garvin began smoking pot, and started selling LSD at Stonewall.
Although on his first visit, Garvin was mostly shocked to see men dancing together, he became a regular and even dated the main doorman (“Blonde Frankie“) for a time. Though he was initially living on the streets and hustling for a living — an experience he would carry with him the rest of his life — he ultimately found his way into living in what David Carter describes in his book Stonewall: The Riots That Sparked the Gay Revolution as a “gay hippie commune.” Garvin began smoking pot, and started selling LSD at Stonewall.
 Most of the people who were at the
Most of the people who were at the 
 In 1964, Rodwell returned to New York and devoted himself to activism for the “homophile” community (as we called ourselves then — I am so glad we don’t use that term anymore). He was volunteering with the Mattachine Society — using his legal name, which was a rarity in that time — and even serving as their vice president. He founded the Mattachine Young Adults organization, and was an early member of the East Coast Homophile Organizations (ECHO) — which coordinated various homophile groups from around the eastern seaboard. On September 19, he and several other notable activists including Randy Wicker, Jefferson Poland, and Renee Cafiero staged a protest against the military’s exclusion of gay service members — and the practice of dishonorably discharging those who were found out. This is officially recognized as the first organized LGBTQ+ protest in United States history (though I suspect there were some before that we just don’t acknowledge).
In 1964, Rodwell returned to New York and devoted himself to activism for the “homophile” community (as we called ourselves then — I am so glad we don’t use that term anymore). He was volunteering with the Mattachine Society — using his legal name, which was a rarity in that time — and even serving as their vice president. He founded the Mattachine Young Adults organization, and was an early member of the East Coast Homophile Organizations (ECHO) — which coordinated various homophile groups from around the eastern seaboard. On September 19, he and several other notable activists including Randy Wicker, Jefferson Poland, and Renee Cafiero staged a protest against the military’s exclusion of gay service members — and the practice of dishonorably discharging those who were found out. This is officially recognized as the first organized LGBTQ+ protest in United States history (though I suspect there were some before that we just don’t acknowledge). In 1966, Rodwell was ejected from a bar called Julius’ for wearing a pin that read “Equality for Homosexuals.” On April 21, with the help of John Timmons and Mattachine president Dick Leitsch, Rodwell held a “sip-in” at the bar. This was specifically to protest a rule by State Liquor Authority that prohibited homosexuals from gathering in places that served alcohol. Rodwell and his cohorts held that the rule encouraged bribery and corruption amongst the police. The publicity from this sit-in led directly to that particular rule ending.
In 1966, Rodwell was ejected from a bar called Julius’ for wearing a pin that read “Equality for Homosexuals.” On April 21, with the help of John Timmons and Mattachine president Dick Leitsch, Rodwell held a “sip-in” at the bar. This was specifically to protest a rule by State Liquor Authority that prohibited homosexuals from gathering in places that served alcohol. Rodwell and his cohorts held that the rule encouraged bribery and corruption amongst the police. The publicity from this sit-in led directly to that particular rule ending. In order to try make the Mattachine Society more accessible, Rodwell proposed they open a storefront. When the idea was rejected, he cut his ties with the organization. In November of 1967, Rodwell opened the Oscar Wilde Memorial Bookshop — the country’s first store that focused on queer authors. The store was so named because Oscar Wilde was the most notable homosexual he could think of and he wanted absolutely not confusion about what the store was all about. The place functioned as more than just a store — Rodwell also envisioned it as a community center that didn’t have age restrictions and didn’t rely on alcohol (or the organized crime families that owned most of the gay bars in the city). To that end, he found the Homophile Youth Movement in Neighborhoods (HYMN) out of the bookshop, and led their rallies in that year. In 1968, he started publishing their periodical HYMNAL. Harvey Milk — now friends with Rodwell — was a frequent customer of the store, and it would later be the inspiration his own shop/community center/campaign headquarters Castro Camera in San Francisco. Rodwell also met Fred Sargeant at his store. Sargeant became heavily involved in HYMN and a romantic relationship blossomed.
In order to try make the Mattachine Society more accessible, Rodwell proposed they open a storefront. When the idea was rejected, he cut his ties with the organization. In November of 1967, Rodwell opened the Oscar Wilde Memorial Bookshop — the country’s first store that focused on queer authors. The store was so named because Oscar Wilde was the most notable homosexual he could think of and he wanted absolutely not confusion about what the store was all about. The place functioned as more than just a store — Rodwell also envisioned it as a community center that didn’t have age restrictions and didn’t rely on alcohol (or the organized crime families that owned most of the gay bars in the city). To that end, he found the Homophile Youth Movement in Neighborhoods (HYMN) out of the bookshop, and led their rallies in that year. In 1968, he started publishing their periodical HYMNAL. Harvey Milk — now friends with Rodwell — was a frequent customer of the store, and it would later be the inspiration his own shop/community center/campaign headquarters Castro Camera in San Francisco. Rodwell also met Fred Sargeant at his store. Sargeant became heavily involved in HYMN and a romantic relationship blossomed. The next day, Rodwell created a flyer — which HYMN helped him to disseminate through Greenwich Village — that read “Get the Mafia and the Cops Out of Gay Bars.” The flyers helped encourage further protests the next several nights — protests Rodwell participated in as well.
The next day, Rodwell created a flyer — which HYMN helped him to disseminate through Greenwich Village — that read “Get the Mafia and the Cops Out of Gay Bars.” The flyers helped encourage further protests the next several nights — protests Rodwell participated in as well.
 In 1978 Rodwell formed Gay People in Christian Science (GPICS) with Ray Spitale, Bob McCullogh, and Bob Mackenroth. While they were not the only gay Christian Science organization in the country, they were the only one actively challenging the church’s policies — actively challenging the excommunication of three of their members. This quickly became Rodwell’s primary focus for his activism. GPICS created an eight-page pamphlet entitled “Gay People in Christian Science?” which they proceeded to mail to every Christian Science church, college organization, and practitioner that they could find. Overall, they mailed out 8,000 copies. They then made plans to hand out the pamphlets at the 1980 Annual Meeting of the Church of Christ, Scientist in Boston. To organize this in the least offensive way possible, Rodwell alerted security for the event of their intentions.
In 1978 Rodwell formed Gay People in Christian Science (GPICS) with Ray Spitale, Bob McCullogh, and Bob Mackenroth. While they were not the only gay Christian Science organization in the country, they were the only one actively challenging the church’s policies — actively challenging the excommunication of three of their members. This quickly became Rodwell’s primary focus for his activism. GPICS created an eight-page pamphlet entitled “Gay People in Christian Science?” which they proceeded to mail to every Christian Science church, college organization, and practitioner that they could find. Overall, they mailed out 8,000 copies. They then made plans to hand out the pamphlets at the 1980 Annual Meeting of the Church of Christ, Scientist in Boston. To organize this in the least offensive way possible, Rodwell alerted security for the event of their intentions.